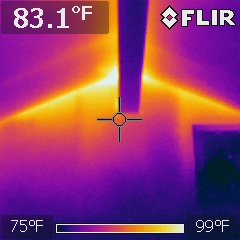
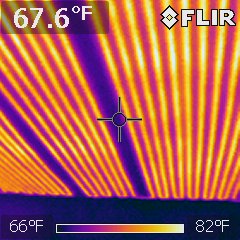
Infrared Thermography
What is Infrared Thermography?
 Infrared Thermography is the process of detecting infrared energy on the surface of an object using an infrared camera. The energy it detects is shown as a temperature. All objects have different properties that affect how much infrared energy it emits and thus what the temperature appears to be. The camera, which should probably be called a detector, is made up of an array of detectors that sense the infrared energy and gives us the reading. The camera does not send out or emit any kind energy or radiation. It does not have X-ray vision, it cannot see through walls or body parts. It just records the surface heat.
Infrared Thermography is the process of detecting infrared energy on the surface of an object using an infrared camera. The energy it detects is shown as a temperature. All objects have different properties that affect how much infrared energy it emits and thus what the temperature appears to be. The camera, which should probably be called a detector, is made up of an array of detectors that sense the infrared energy and gives us the reading. The camera does not send out or emit any kind energy or radiation. It does not have X-ray vision, it cannot see through walls or body parts. It just records the surface heat. 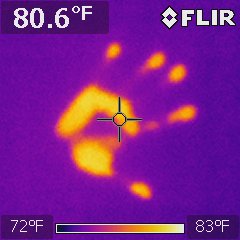 The detectors are extraordinarily sensitive to heat energy. The picture is of my hand placed on a wall for 3 seconds and removed. The picture captured the residual heat signature.
The detectors are extraordinarily sensitive to heat energy. The picture is of my hand placed on a wall for 3 seconds and removed. The picture captured the residual heat signature.
What are the Advantages of Infrared Thermography?
Infrared or Thermal imaging is a technology that allows the inspector to show you things about your home that no one can show you using other inspection methods. Thermal imaging produces images of invisible heat energy emitted from objects and systems in the home and allows us to measure it. Thermal imaging helps us to diagnose the problem rather than merely identify symptoms and can sometimes, but not always, identify and document:
- Electrical faults before they cause a fire;
- Overloaded and undersized circuits;
- Circuit breakers in need of immediate replacement;
- Missing, deficient, damaged, and or wet insulation;
- Heat loss and air infiltration in walls, ceilings, floors, windows and doors, water;
- Moisture intrusion that could lead to mold;
- Hidden roof leaks before they cause serious damage;
- Air conditioner compressor leaks;
- Structural defects;
- Dangerous flue leaks;
- Damaged and or malfunctioning radiant heating systems;
- Unknown plumbing leaks;
- Overheated equipment.
What are the Limitations of Infrared Thermography
There are many factors that affect the kind of image you get when taking an infrared image. The main factor is probably the temperature difference between the object and adjacent material. This is referred to as Delta T. Delta in the science community just means change, so Delta T refers to the change or difference in temperature. For the infrared camera to give a fairly clear picture of an anomaly, we like a temperature difference of 10°F -15°F. It does not matter if the temperature is 55°F outside and 70°F inside or 70°F inside and 85°F outside, just so we can get the temperature difference.
Some materials are good emitters of infrared heat where other materials reflect infrared heat. Materials such as brick, concrete, formica, white paper, plywood, and water are great emitters. Shining materials such as glass and metals reflect infrared energy and do not give an accurate representation of heat. Rough surfaces are a better emitter than smooth surfaces that reflect energy.
Following are infrared pictures of various materials and systems.